

Attempts at in vitro fertilization date as back as 1953 however The first pregnancy achieved through in vitro human fertilization of a human oocyte was reported in The Lancet from the Monash University team of Carl Wood, John Leeton and Alan Trounson in 1973, It lasted only a few days, biochemical pregnancy.
There was also an ectopic pregnancy reported by Patrick Steptoe and Robert Edwards in 1976.
In 1977, Steptoe and Edwards successfully carried out a pioneering conception which resulted in the birth of the world’s first baby to be conceived by IVF, Louise Brown on 25 July 1978, in Oldham General Hospital, Greater Manchester, UK.
The first child born from gamete micromanipulation was a child in Singapore born in April 1989.
The technique was developed by Gianpiero Palermo at the Vrije Universiteit Brussel, in the Center for Reproductive Medicine headed by Paul Devroey and Andre Van Steirteghem.
The procedure itself was first performed in 1987, It grew up to the pronuclear stage. The first activated embryo by ICSI was produced in 1990, but the first successful birth by ICSI took place on January 14, 1992.
Ovaries are stimulated by hormones (FSH, HMG) to promote growth of follicles containing eggs.
Ovaries are stimulated by hormones (FSH, HMG) to promote growth of follicles containing eggs.
When the ovarian follicles have reached complete growth, induction of final oocyte maturation is performed, generally by an injection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). hCG acts as an analog of the luteinizing hormone causes final follicular maturation and release of oocyte and surrounding cumulus in the follicle. The ovulation is imminent between 38 and 40 hours after a single HCG injection, The egg retrieval is performed at a time usually between 34 and 36 hours after hCG injection, prior to when the follicles would rupture.
This procedure is done under anesthesia.
The eggs are retrieved from the patient using transvaginal sonography. The pickup needle pierces vaginal wall under sonography guidance, reaches follicles. The follicles are aspirated, and the follicular fluid is passed to an embryologist for identification of oocyte.
Semen is prepared for fertilization by removing inactive cells and seminal fluid by centrifugation…. Semen wash.
Eggs and sperms are incubated in appropriate culture media.
Fertilization is checked after 16-18 hours.
Fertilized eggs are incubated for 48-72 hours
After semen wash, motile sperms are selected for ICSI. Sperms are immobilized by PVP or sperm slow ( selection of mature sperms with fewer DNA strand breaks and genetic abnormality ) and selected for the procedure.
It is done by specialized inverted microscope called Micromanipulator.
A holding pipette stabilizes oocyte by gentle suction created by a microinjector.
Hollow glass micropipette is used to cut the tail of immobilized sperm.
The oocyte is pierced and sperm is released in the cytoplasm.
The post-procedure oocyte is placed in culture and incubated, checked for signs of fertilization after 16-18 hours.
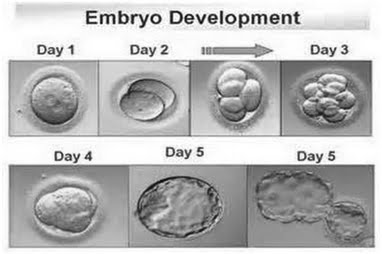
Embryos are cultured in incubator till cleavage stage ( Day 2-3 ) or Blastocyst stage ( Day 5-6 ).
The blastocyst has an advantage of higher implantation and ongoing pregnancy rate.
Embryo or oocytes are graded commonly by morphologic features, amount of cells, evenness of growth and fragmentation before transfer.

Selected embryos are placed in the uterine cavity by thin plastic catheter under sonography guidance. A number of embryos transferred depend on availability and National regulation.
Post-transfer hormonal support is given in the form of HCG and progesterone for 15 days after which a blood pregnancy test is done.
Good quality excess embryos are frozen and stored. These frozen embryos can be thawed for subsequent cycles.